 | | | Switch to: Europe, USA, New Zealand, Antarctica Credit: NOAA/Ovation  Planetary K-index Planetary K-index
Now: Kp= 2.33 quiet
24-hr max: Kp= 3.00 quiet
explanation | more data
Interplanetary Mag. Field
Btotal: 6.71 nT
Bz: -3.56 nT south
more data: ACE, DSCOVR
Updated: Today at 1146 UT  Coronal Holes: 09 Apr 24 Coronal Holes: 09 Apr 24 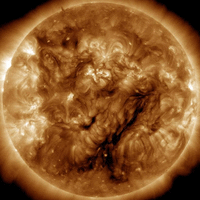
There are no significant equatorial coronal holes on the Earthside of the sun. Credit: SDO/AIA  Polar Stratospheric Clouds
Colorful Type II polar stratospheric clouds (PSC) form when the temperature in the stratosphere drops to a staggeringly low -85C. NASA's MERRA-2 climate model predicts when the air up there is cold enough: 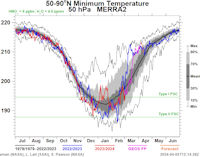
On Apr. 06, 2024, the Arctic stratosphere is much too warm for Type II polar stratospheric clouds. | more data. Noctilucent Clouds
The southern season for NLCs is over. The first clouds were detected inside the Antarctic Circle on Dec. 4, 2023, by the NOAA 21 satellite. The same satellite detected the last cloud on Feb. 21, 2024. Daily maps are now blank:
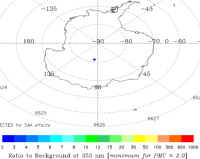
Updated: Feb 22, 2024
An instrument onboard NOAA 21 (OMPS LP) is able to detect NLCs (also known as "polar mesospheric clouds" or PMCs). Now that the southern season has ended, attention turns to the northern hemisphere. The first NLCs should appear inside the Arctic Circle in mid to late May.
 SPACE WEATHER
NOAA Forecasts | | Updated at: 2024 Apr 10 2200 UTC FLARE | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | CLASS M | 10 % | 25 % | CLASS X | 01 % | 05 % |  Geomagnetic Storms: Geomagnetic Storms:
Probabilities for significant disturbances in Earth's magnetic field are given for three activity levels: active, minor storm, severe storm Updated at: 2024 Apr 10 2200 UTC Mid-latitudes | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | ACTIVE | 20 % | 10 % | MINOR | 05 % | 01 % | SEVERE | 01 % | 01 % | High latitudes | 0-24 hr | 24-48 hr | ACTIVE | 15 % | 15 % | MINOR | 30 % | 20 % | SEVERE | 25 % | 15 % | | | |  | | | | | | | | | | | This is an AI Free Zone! Text created by Large Language Models is spreading rapidly across the Internet. It's well-written, artificial, frequently inaccurate. If you find a mistake on Spaceweather.com, rest assured it was made by a real human being. | | | QUIET WITH A CHANCE OF FLARES: The sun has not produced a significant solar flare in more than a week. The best chance for a break in the quiet is sunspot AR3633; it has a 'beta-gamma' magnetic field that harbors energy for M-class explosions. NOAA forecasters say there is a 25% chance of an M-flare today. Solar flare alerts: SMS Text THIS COMET DID NOT SURVIVE THE ECLIPSE: Astronomer Karl Battams of the Naval Research Lab predicted that a sungrazing comet might be visible during Monday's total eclipse. He was right. Chinese amateur astronomer Lin Zixuan was in New Hampshire for the eclipse, and he photographed the disintegrating comet: 
Named "SOHO-5008", the comet had been discovered earlier the same day by amateur astronomer Worachate Boonplod, who noticed it in SOHO coronagraph images. Battams quickly realized that the comet might be bright enough to photograph in the otherworldly twilight of the Moon's shadow. "Ground-based observations of sungrazing comets are extremely rare, so this would be a great opportunity to see an eclipse comet!" says Battams. Soon after Zixuan photographed the comet, it disintegrated. SOHO has seen this happen more than 5000 times. Most doomed sungrazers (including this one) are members of the Kreutz family. Named after a 19th century German astronomer who studied them in detail, Kreutz sungrazers are fragments from the breakup of a giant comet ~2000 years ago. Several fragments pass by the sun and disintegrate every day, although most are too small to see. 
A SOHO coronagraph image of the disintegrating comet
Battams can recall only two other examples of sungrazers seen during a solar eclipse-- one in 2020 (also a Worachate Boonplod discovery) and another in 2008. " I think with modern imaging equipment and techniques, seeing a sungrazer during an eclipse is no longer hugely challenging, but it does require one crucial ingredient: the right comet at the right time. We got lucky this week!" he says. Realtime Solar Eclipse Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
AMBER DRAGONFLY SPACE PENDANT: This dragonfly has touched space. The students of Earth to Sky Calculus launched it to the stratosphere onboard a cosmic ray research balloon, 109,228 feet above California's Sierra Nevada: 
You can have it for $179.95. Made of genuine Baltic Amber with a sterling silver exoskeleton, the pendant measures 1 1/4 inch and comes with a matching 18-inch sterling silver chain. The wings of the dragonfly include four pieces of natural amber colored Cognac, Olive Green and Honey Yellow. The students are selling space pendants to pay the helium bill for their cosmic ray ballooning program. Each one comes with a greeting card showing the jewelry in flight and telling the story of its trip to the stratosphere and back again.
Far Out Gifts: Earth to Sky Store
All sales support hands-on STEM education
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter
Realtime Comet Photo Gallery
Free: Spaceweather.com Newsletter Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com. On Apr 09, 2024, the network reported 2 fireballs.
(2 sporadics) 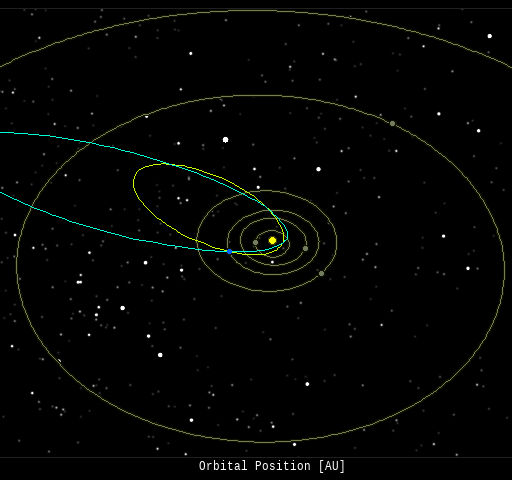 In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies] Potentially Hazardous Asteroids ( PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding new ones all the time. On April 10, 2024 there were 2349 potentially hazardous asteroids.
 | Recent & Upcoming Earth-asteroid encounters: | Asteroid | Date(UT) | Miss Distance | Velocity (km/s) | Diameter (m) | | 2024 FD4 | 2024-Apr-05 | 5.6 LD | 4.1 | 12 | | 2024 GO | 2024-Apr-05 | 2.2 LD | 29.5 | 18 | | 2024 GN1 | 2024-Apr-05 | 10.3 LD | 13.1 | 20 | | 2024 GF | 2024-Apr-05 | 4.5 LD | 6.1 | 14 | | 2024 GA | 2024-Apr-05 | 4.1 LD | 3.2 | 11 | | 2024 GG | 2024-Apr-05 | 15 LD | 5.6 | 16 | | 2014 GF1 | 2024-Apr-07 | 20.1 LD | 7.8 | 22 | | 2024 FG | 2024-Apr-07 | 12.4 LD | 9.8 | 55 | | 2024 GJ1 | 2024-Apr-07 | 13.7 LD | 11.2 | 26 | | 2024 GE2 | 2024-Apr-07 | 4.4 LD | 4.7 | 9 | | 2024 FH2 | 2024-Apr-07 | 16 LD | 19.7 | 120 | | 2024 GB | 2024-Apr-07 | 13.7 LD | 9 | 54 | | 2024 ED6 | 2024-Apr-08 | 5.5 LD | 6.7 | 52 | | 2024 GQ | 2024-Apr-08 | 5.6 LD | 9.9 | 13 | | 2005 FG | 2024-Apr-08 | 18.4 LD | 5.5 | 57 | | 2020 BP13 | 2024-Apr-09 | 15.2 LD | 6.8 | 209 | | 2024 GQ1 | 2024-Apr-09 | 1.4 LD | 13.4 | 7 | | 2024 FT2 | 2024-Apr-10 | 11.8 LD | 11.9 | 32 | | 2024 GJ2 | 2024-Apr-11 | 0 LD | 14.4 | 3 | | 2024 GA2 | 2024-Apr-12 | 14.4 LD | 14 | 32 | | 2021 RJ19 | 2024-Apr-12 | 19.6 LD | 11.4 | 25 | | 2024 FX3 | 2024-Apr-12 | 9.5 LD | 11.7 | 29 | | 2021 GQ5 | 2024-Apr-13 | 8.8 LD | 7.5 | 7 | | 2024 FP3 | 2024-Apr-13 | 2.7 LD | 6.3 | 21 | | 2024 GA1 | 2024-Apr-14 | 9.5 LD | 18.1 | 54 | | 2023 FN13 | 2024-Apr-14 | 3.3 LD | 4.9 | 13 | | 2022 UO1 | 2024-Apr-14 | 16.7 LD | 14 | 33 | | 2024 GW | 2024-Apr-15 | 11.2 LD | 8.7 | 26 | | 2024 GL2 | 2024-Apr-15 | 10.9 LD | 8.6 | 13 | | 2024 GO1 | 2024-Apr-15 | 8.5 LD | 9.1 | 12 | | 517681 | 2024-Apr-15 | 18.4 LD | 14.2 | 589 | | 439437 | 2024-Apr-15 | 8.5 LD | 16.5 | 609 | | 2024 FJ4 | 2024-Apr-15 | 14.3 LD | 9.5 | 33 | | 2024 GN2 | 2024-Apr-16 | 1.2 LD | 18.5 | 17 | | 2024 GM1 | 2024-Apr-17 | 3.5 LD | 10.4 | 28 | | 2024 FF4 | 2024-Apr-18 | 16.1 LD | 13 | 52 | | 2023 HU3 | 2024-Apr-18 | 15.9 LD | 19.1 | 35 | | 2024 FU4 | 2024-Apr-19 | 19.2 LD | 7.5 | 30 | | 2021 JW2 | 2024-Apr-19 | 1.6 LD | 5.1 | 11 | | 2017 SA20 | 2024-Apr-19 | 3.8 LD | 6.2 | 8 | | 2024 FT4 | 2024-Apr-19 | 19.3 LD | 5.2 | 21 | | 2024 GM | 2024-Apr-21 | 18.7 LD | 10.8 | 86 | | 2021 VH2 | 2024-Apr-25 | 9.3 LD | 2.7 | 6 | | 2024 FG5 | 2024-Apr-26 | 12.5 LD | 9.1 | 37 | | 2024 GR1 | 2024-Apr-27 | 19.6 LD | 7.2 | 53 | | 2021 GD3 | 2024-Apr-30 | 11.4 LD | 3.5 | 14 | | 2022 TN1 | 2024-Apr-30 | 18.6 LD | 17.7 | 295 | | 2022 AA5 | 2024-May-02 | 12 LD | 8.9 | 67 | | 2024 FR5 | 2024-May-05 | 4.9 LD | 5.2 | 50 | | 2021 JG9 | 2024-May-10 | 16.9 LD | 16.1 | 32 | | 2016 FT14 | 2024-May-10 | 19.9 LD | 5.9 | 39 | | 2015 KJ19 | 2024-May-14 | 15.8 LD | 23.1 | 112 | | 2014 WF6 | 2024-May-14 | 7.2 LD | 18.9 | 47 | | 2021 JN10 | 2024-May-14 | 17.5 LD | 13.2 | 33 | | 2021 JJ | 2024-May-15 | 17.2 LD | 5.8 | 28 | | 2022 WN2 | 2024-May-17 | 13.7 LD | 5.5 | 6 | | 2019 VB5 | 2024-May-21 | 7.8 LD | 6.3 | 2 | | 2008 LD | 2024-May-28 | 7.7 LD | 4.5 | 6 | | 2021 LV | 2024-May-29 | 12 LD | 15.5 | 9 | | 1998 KY26 | 2024-Jun-01 | 12 LD | 5.3 | 27 | | 2016 JC6 | 2024-Jun-01 | 19.9 LD | 7.1 | 188 | | 2008 YN2 | 2024-Jun-05 | 10.5 LD | 7.7 | 20 | | 2021 LW3 | 2024-Jun-06 | 9.7 LD | 9.8 | 86 | Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. | | Cosmic Rays in the Atmosphere | SPACE WEATHER BALLOON DATA: Almost once a week, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus fly space weather balloons to the stratosphere over California. These balloons are equipped with sensors that detect secondary cosmic rays, a form of radiation from space that can penetrate all the way down to Earth's surface. Our monitoring program has been underway without interruption for 7 years, resulting in a unique dataset of in situ atmospheric measurements. Latest results (July 2022): Atmospheric radiation is decreasing in 2022. Our latest measurements in July 2022 registered a 6-year low: 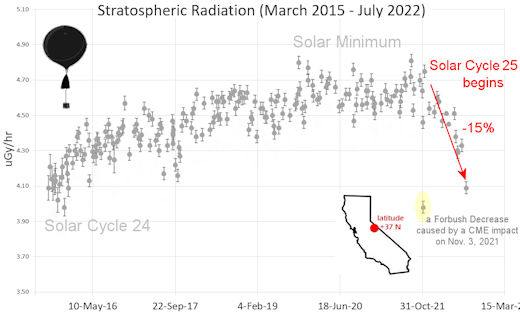
What's going on? Ironically, the radiation drop is caused by increasing solar activity. Solar Cycle 25 has roared to life faster than forecasters expected. The sun's strengthening and increasingly tangled magnetic field repels cosmic rays from deep space. In addition, solar coronal mass ejections (CMEs) sweep aside cosmic rays, causing sharp reductions called "Forbush Decreases." The two effects blend together to bring daily radiation levels down. .Who cares? Cosmic rays are a surprisingly "down to Earth" form of space weather. They can alter the chemistry of the atmosphere, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. According to a study from the Harvard T.H. Chan school of public health, crews of aircraft have higher rates of cancer than the general population. The researchers listed cosmic rays, irregular sleep habits, and chemical contaminants as leading risk factors. A number of controversial studies (#1, #2, #3, #4) go even further, linking cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Technical notes: The radiation sensors onboard our helium balloons detect X-rays and gamma-rays in the energy range 10 keV to 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners. Data points in the graph labeled "Stratospheric Radiation" correspond to the peak of the Regener-Pfotzer maximum, which lies about 67,000 feet above central California. When cosmic rays crash into Earth's atmosphere, they produce a spray of secondary particles that is most intense at the entrance to the stratosphere. Physicists Eric Regener and Georg Pfotzer discovered the maximum using balloons in the 1930s and it is what we are measuring today. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau | | | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. | | | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. | | | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory | | | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. | | | information about sunspots based on the latest NOAA/USAF Active Region Summary | | | current counts of failed and deployed Starlink satellites from Jonathan's Space Page. See also, all satellite statistics. | | | Authoritative predictions of space junk and satellite re-entries | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | fun to read, but should be taken with a grain of salt! Forecasts looking ahead more than a few days are often wrong. | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | the underlying science of space weather |  | When looking for casinos to play online when the weather is bad, you can try the SkyCity Online Casino if you are located in New Zealand. If you are not from NZ you can try the Swedish page Svenska casino online to find suitable games, check out svenskacasinoonline.net. Always check your local laws before playing with real money.. |  | BestCSGOGambling is the best site for everything related to CSGO gambling on the web | | | These links help Spaceweather.com stay online. Thank you to our supporters! | | | | | | | | |  | |  |   | ©2021 Spaceweather.com. All rights reserved. This site is penned daily by Dr. Tony Phillips. | |

