When is the best time to see auroras? Where is the best place to go? And how do you photograph them? These questions and more are answered in a new book, Northern Lights - a Guide, by Pal Brekke & Fredrik Broms. | | | COMET ISON LIVES (UPDATED): Cancel the funeral. Comet ISON is back from the dead. Yesterday, Nov. 28th, Comet ISON flew through the sun's atmosphere and appeared to disintegrate before the cameras of several NASA and ESA spacecraft. This prompted reports of the comet's demise. Today, the comet has revived and is rapidly brightening. Click to view a SOHO coronagraph movie of the solar flyby (updated Nov. 29 @ 1800 UT): 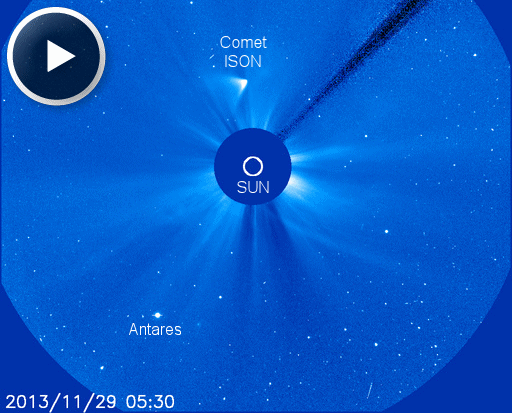
Before the flyby, experts had made many predictions about what might happen to the comet, ranging from utter disintegration to glorious survival. No one predicted both. Karl Battams of NASA's Comet ISON Observing Campaign says, "[colleague] Matthew Knight and I are ripping our hair out right now as we know that so many people in the public, the media and in science teams want to know what's happened. We'd love to know that too! Right now, here's our working hypothesis: "As comet ISON plunged towards to the Sun, it began to fall apart, losing not giant fragments but at least a lot of reasonably sized chunks. There's evidence of very large dust in the long thin tail we saw in the [SOHO coronagraph] images. Then, as ISON plunged through the corona, it continued to fall apart and vaporize, losing its coma and tail completely just like sungrazing Comet Lovejoy did in 2011. What emerged from the Sun was a small but perhaps somewhat coherent nucleus that has resumed emitting dust and gas for at least the time being." Battams emphasizes that it is too soon to tell how big the remnant nucleus is or how bright the resurgent comet will ultimately become. "We have a whole new set of unknowns, and this ridiculous, crazy, dynamic and unpredictable object continues to amaze, astound and confuse us to no end. We ask that you please be patient with us for a couple of days as we analyze the data and try to work out what is happening." Astrophotographer Babak Tafreshi has edited an HD video that compares views of ISON from both of SOHO's coronagraphs. "It seems the comet could become a naked eye object with several degrees of scattered tail by Dec 2nd or 3rd," he predicts. "It's not the comet of the century for sure, and fainter than the Lovejoy sungrazer in Dec. 2011, but an interesting imaging target is just a few nights away!" Solar flare alerts: text, voice Realtime Comet ISON Photo Gallery
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com. On Nov. 29, 2013, the network reported 25 fireballs.
(23 sporadics, 1 Quadrantid, 1 November omega Oriond) 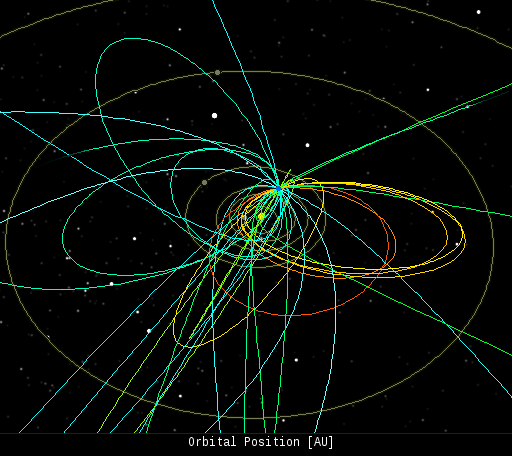
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies] Potentially Hazardous Asteroids ( PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding new ones all the time. On November 29, 2013 there were potentially hazardous asteroids. Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau | | | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. | | | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. | | | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory | | | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. | | | from the NOAA Space Environment Center | | | the underlying science of space weather | | 
