Listen to radar echoes from satellites and meteors, live on listener-supported Space Weather Radio. | | |
RARE DOUBLE-COMET FLYBY OF MERCURY: NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft is about to get a close-up view of Comet ISON's outburst. On Nov. 18-19 Comet ISON and Comet Encke both will fly by Mercury, the planet MESSENGER is orbiting. You can learn more about this rare double-comet flyby and what MESSENGER might see in a video from Science@NASA.
SPRAWLING SUNSPOT, CHANCE OF FLARES: Sunspot AR1897 has evolved into a sprawling archipelago of magnetic islands with more than a dozen dark cores scattered across 350,000 km of solar "terrain." This complex region has a 'beta-gamma-delta' magnetic field that harbors energy for X-class solar flares, and it is directly facing Earth:
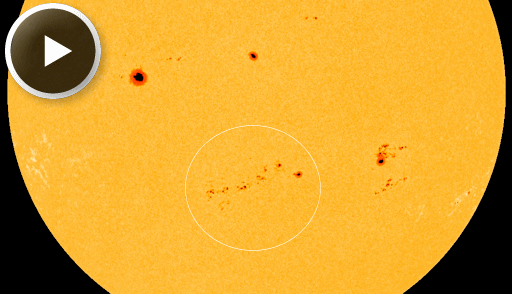
Any eruptions from AR1897 this weekend would likely be geoeffective. NOAA forecasters estimate a 60% chance of M-class solar flares and a 15% chance of X-flares on Nov. 16th. Solar flare alerts: text, voice
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
COMET ISON UPDATE: Reports of naked-eye sightings of Comet ISON are coming in from around the world. Experienced observers put the comet's magntitude at +5.5 on Nov. 16th. This means it is now fully 10 times brighter than it was only three days ago before the outburst. To the naked eye, ISON appears as a faint smudge of pale green light low in the pre-dawn sky. The view through a telescope is more dramatic. The comet's tail has become a riotous crowd of gaseous streamers stretching more than 3.5 degrees across the sky. Amateur astronomer Waldemar Skorupa sends this picture from Kahler Asten, Germany:
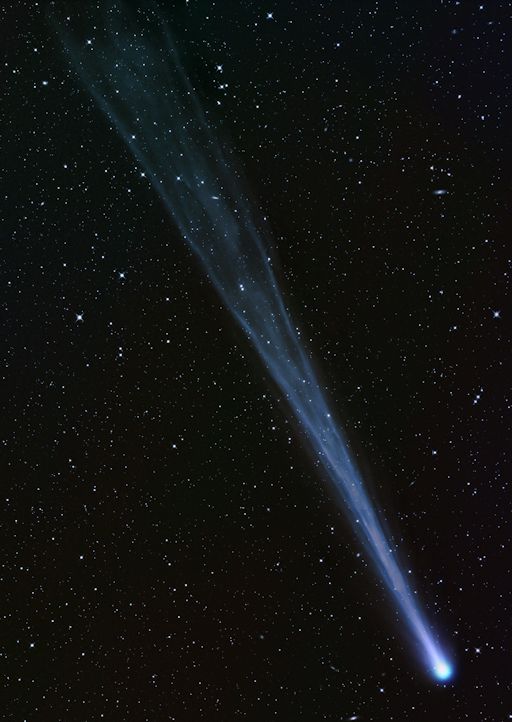

The tail is so long, he couldn't fit the whole thing in the field of view. How long is it? Comet ISON's tail extends more than 8 million kilometers behind the comet's nucleus. For comparison, that's 21 times the distance between Earth and the Moon.
Because so much gas and dust is spewing from the comet's core, it is impossible to see clearly what caused Comet ISON's outburst on Nov. 13-14. One possibility is that fresh veins of ice are opening up in the comet's nucleus, vaporizing furiously as ISON approaches the sun. Another possibility is that the nucleus has completely fragmented.
"If so, it will still be several days before we know for sure," says Karl Battams, an astronomer with NASA's Comet ISON Observing Campaign. "When comet nuclei fall apart, it’s not like a shrapnel-laden explosion. Instead, the chunks slowly drift apart at slightly different speeds. Given that ISON’s nucleus is shrouded in such a tremendous volume of light-scattering dust and gas right now, it will be almost impossible to determine this for at least a few days and perhaps not until the comet reaches the field of view of NASA's STEREO HI-1A instrument on November 21, 2013. We will have to wait for the chunks to drift apart a sufficient distance, assuming they don't crumble first."
In short, no one knows for sure what is happening to Comet ISON. This could be the comet's death throes--or just the first of many brightening events the comet experiences as it plunges toward the sun for a close encounter on Thanksgiving Day (Nov. 28th).
Monitoring is encouraged. Comet ISON rises in the east just before the sun. Amateur astronomers, if you have a GOTO telescope, enter these coordinates. Dates of special interest include Nov. 17th and 18th when the comet will pass the bright star Spica, making ISON extra-easy to find. Sky maps: Nov. 15, 16, 17, 18, 19.
Realtime Comet ISON Photo Gallery
Ephemerides: Comet ISON, Comet Lovejoy, Comet Encke, Comet LINEAR X1
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Realtime Comet ISON Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of
NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com.
On Nov. 16, 2013, the network reported 10 fireballs.
(7 sporadics, 2 Leonids, 1 Northern Taurid)
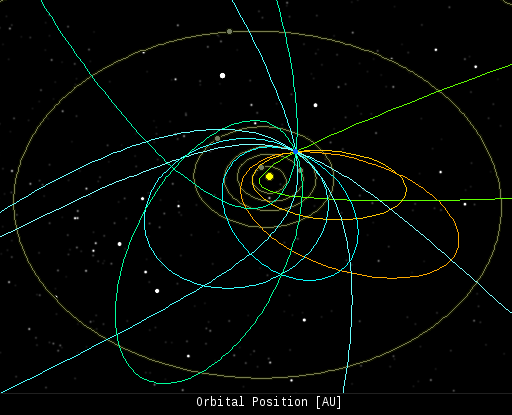
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On November 16, 2013 there were 1439 potentially hazardous asteroids.
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |

