Listen to radar echoes from satellites and meteors, live on listener-supported Space Weather Radio. | | |
EVENING LIGHTS: When the sun goes down tonight, step outside and look west. The crescent Moon, Mars, Saturn, and first-magnitude star Spica have converged there in a loose but beautiful grouping of bright evening lights. It's a nice way to end the day. [sky map]
MAGNETIC BRIDGE: Sunspots AR1528 and AR1529 appear to be far apart. More than 200,000 km of stellar surface separate the two. Nevertheless, they are connected by a tubular bridge of magnetism. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) photographed the vast structure on July 24th:
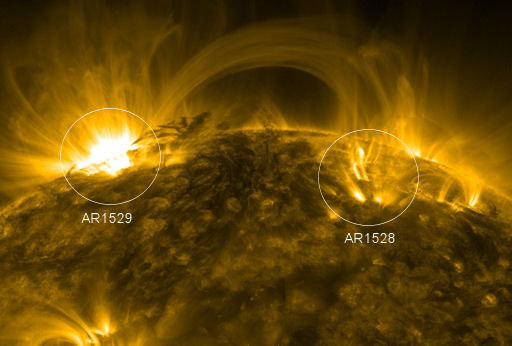
This extreme ultraviolet image traces the bridge via the glow of hot plasma it contains. Material can flow back and forth inside the tube, allowing one sunspot to respond to what the other is doing.
Researchers once thought that sunspots were independent operators, but SDO has shown over and over again that widely-spaced sunspots can be linked. An eruption in one can set off an explosion in another, leading to a chain reaction that can spread around the circumference of the sun. The global eruption of August 2010 is a memorable example.
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
VERY FAST FARSIDE CME (UPDATED): On July 23rd, a coronal mass ejection (CME) blasted away from the sun with rare speed: 3400 km/s or 7.6 million mph. CMEs moving this fast occur only once every ~5 to 10 years. The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory recorded the cloud's rapid departure from the sun:

The source of the CME was sunspot AR1520, which sparked many bright auroras earlier this month when it was on the Earthside of the sun. Now, however, the active region is transiting the sun's farside so this blast was not geoeffective. One can only imagine the geomagnetic storms such a fast CME could produce if it were heading our way.
Update: According to a forecast track prepared by analysts at the Goddard Space Weather Lab, this CME will miss all of the solar system's inner planets.
Realtime Noctilucent Cloud Photo Gallery
[previous years: 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2011]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On July 24, 2012 there were potentially hazardous asteroids.
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |

