Metallic photos of the sun by renowned photographer Greg Piepol bring together the best of art and science. Buy one or a whole set. They make a stellar gift. | | |
ASTEROID FLYBY: NASA radars are monitoring 2005 YU55, an asteroid the size of an aircraft carrier, as it heads for a Nov. 8th flyby of the Earth-Moon system. There is no danger to our planet. At closest approach on Tuesday at 3:28 pm PST (23:28 UT), the 400m-wide space rock will be 324,600 kilometers away, about 85% the distance from Earth to the Moon.
Professional astronomers are eagerly anticipating the flyby as the asteroid will present an exceptionally strong radar target. Powerful transmitters at Goldstone and Arecibo will ping the space rock as it passes by, revealing the asteroid's shape and texture in crisp detail, and pinpointing its orbit for future flyby calculations. A movie from JPL explains:
Asteroids this big have passed by Earth at similar distances many times before, but this is the first time astronomers have known about the flyby in advance. For instance, a similar encounter occurred in 1976 when 2010 XC15 split the distance between Earth and the Moon. Researchers didn't discover that space rock until 24 years after the flyby. The Nov. 8, 2011, passage of 2005 YU55 thus represents a rare opportunity for asteroid research.
Experienced amateur astronomers should be able to photograph 2005 YU55 as it zips through the constellations Aquila and Pegasus glowing like an 11th magnitude star. Even under the full moonlight of Nov. 8th, such a bright asteroid is within reach of mid-sized backyard telescopes. The timing of the flyby favors observers in western Europe and eastern parts of North America. Check Sky & Telescope for observing tips or go straight to JPL for the object's ephemeris.
SOLAR ACTIVITY: Sunspot AR1339 is crackling with M-class solar flares, unleashing at least five of them in the past 24 hours. The blasts have been coming with such thick frequency that photographer Randy Shivak of Elyria, Ohio, was able to catch one in action on Nov. 5th:

"Looking like iron filings around a bar magnet, sunspot group 1339 showed itself in the throes of a solar flare," says Shivak.
Even bigger eruptions are possible before the weekend is over. AR1339 has a delta-class magnetic field that harbors energy for X-class flares. The sunspot is turning toward Earth, so the odds of a geoeffective flare are increasing. Solar flare alerts: text, voice.
more images: from Sheri Lynn Karl of Aberdeen, Scotland; from Monika Landy-Gyebnar of Veszprem, Hungary; from Lyrics of Shiqi, Shiqiao, Panyu district, Guangzhou, China; from Juerg Alean of Eglisau, Switzerland; from Andrew Neilson of Glasgow, Scotland, UK; from Dennis Simmons of Brisbane, Qld, Australia; from Alan Friedman of Buffalo, NY; from Dennis Put of Brielle, The Netherlands; from Michael Borman of Evansville, Indiana; from Sternwarte Riesa of Riesa, Saxony, Germany; from Paul Evans of Larne, Co Antrim, Northern Ireland;
NORTHERN LIGHTS: On Friday night, sky watchers in Scandinavia witnessed a vivid display of green auroras. It was so bright, even the rocks and water got involved:
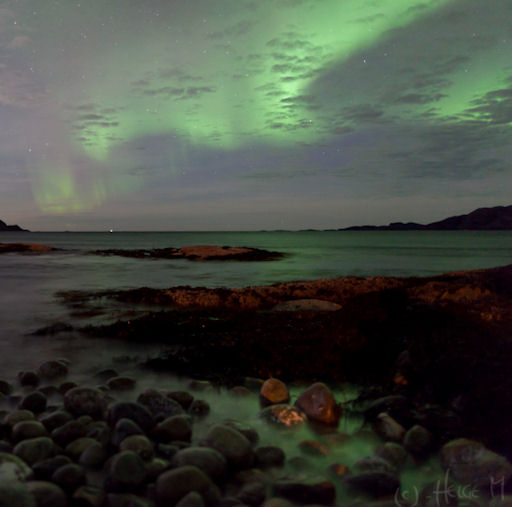

"After weeks with rain and overcast, it was good to see the auroras again," says photographer Helge Mortensen of Kvaløya, Norway. "An exposure time of only 4 to 5 seconds was sufficient to reveal the water's green cast."
The display was caused by the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF), which tipped south and partially canceled Earth's own north-pointing field. This created a crack in Earth's magnetosphere; solar wind flowed in to fuel the auroras. Aurora alerts: text, voice.
more images: from Ole C. Salomonsen of Tromsø, Norway, from Frank Olsen of Blokken, Norway; from Sindre Nedrevåg of Bodoe, Norway; from the DMSP F18 satellite in Earth orbit
October 2011 Aurora Gallery
[previous Octobers: 2010, 2009, 2008, 2007, 2006, 2004, 2003, 2002]

