| COSMIC RAYS HIT SPACE AGE HIGH: NASA spacecraft are measuring record-high levels of cosmic rays--a side-effect of the deepest solar minimum in nearly a century. This development could have implications for the amount of shielding astronauts need to take when they explore deep space. Science@NASA has the full story. PRETTY SKY ALERT: Tonight when the sun goes down, step outside and look up. You might see something like this: 
"The Moon and Jupiter are very close together tonight," says Monika Landy-Gyebnar, who took this picture just hours ago from Veszprém, Hungary. "The beautiful pair of the evening sky twinkled brightly above our town's viaduct, no matter how the streetlights tried to overshine them." There's nothing astronomically significant about this meeting of heavenly lights--just very pretty. Don't miss it: sky map. more images: from Mustafa Erol of Antalya, Turkey; from Jens Hackmann of Bad Mergentheim, Germany; from M. Raşid Tuğral of Ankara-Turkiye; from Peter von Bagh of Porvoo, Finland; from Giuseppe Pappa of Mascalucia, Sicily, Italy; from Christophe Stolz of near Bern, Switzerland SPACE WEATHER ON MERCURY: Today, NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft is going to fly by Mercury only 142 miles from the planet's surface. Naturally, much attention will be given to pictures of new craters and previously unseen terrain, but there is another, equally sensational reason for the flyby--namely, to investigate Mercury's hyperactive space weather: 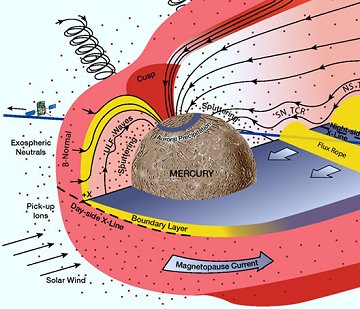
Mercury's magnetic field is buffeted by solar wind as much as fifteen times stronger than the solar wind we experience at Earth. During an earlier flyby of Mercury in Oct. 2008, MESSENGER encountered magnetic "tornadoes" – twisted bundles of magnetic fields connecting Mercury to interplanetary space. The twisters are formed by explosive magnetic reconnection events at the solar wind-magnetic field boundary. Solar wind can actually flow down the throats of these tornadoes to strike and erode the surface of Mercury, giving Mercury a comet-like tail. MESSENGER will fly right through this maelstrom of magnetism and solar wind en route to buzzing Mercury's surface. Stay tuned for data!
Sept. 2009 Aurora Gallery
[previous Septembers: 2008, 2007, 2006, 2005, 2004, 2002, 2001]
Explore the Sunspot Cycle | 
