Lights Over Lapland is excited to announce that our aurora webcam will be up and running 365 days per year! You can now enjoy watching the Midnight Sun and all of the other drama in the sky above Abisko National Park, Sweden here. | | |
INCOMING SOLAR WIND STREAM: A stream of solar wind is approaching Earth and it could graze our planet's magnetic field on April 26th or 27th. The gaseous material is flowing from a northern hole in the sun's atmosphere. The stream won't hit our planet head on, but sometimes grazing impacts produce interesting effects--for instance, making Earth's magnetosphere ring like a bell. Free: Aurora Alerts
CELL PHONE CAPTURES ISS TRANSIT: Catching the International Space Station (ISS) as it crosses in front of the sun has become a favorite challenge for many astrophotographers. The silhouette of the giant spacecraft is like a large sunspot, theoretically easy to photograph, but tricky in practice because ISS transits last only a split second. Now, perhaps for the first time, someone has done it using a cell phone camera. Norman Carlson sends this image from Douglas, Arizona:
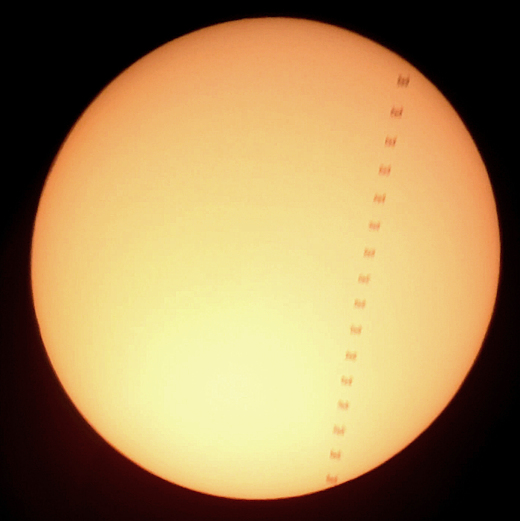

"Of course, there are sharper, clearer images on SpaceWeather.com of ISS transits across the sun, but probably not many that used a cell phone camera to record the passage," says Carlson. "Because the transit only lasted 0.58 seconds, I used the video mode of the cell phone camera at 30 frames per second, and mounted the cell phone over the eyepiece of a 6-inch Dobsonian reflector with a solar filter. Watching on the screen of the phone, I didn't see it dart by. On a computer monitor, though, and slowed down, it's clearly identifiable as the ISS."
Carlson knew when and where to look using predictions from Calsky.com. "Not bad for a cell phone camera," he says.
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
RADIO STORM ON JUPITER: Yesterday, a radio storm happened on Jupiter. Astronomers have known since 1954 that the giant planet sometimes produces powerful bursts of shortwave static. Thomas Ashcraft recorded such a burst on April 24th using his amateur radio telescope in New Mexico. Click to hear the crackling "swooshes" that filled his observatory during the 2 hour storm:
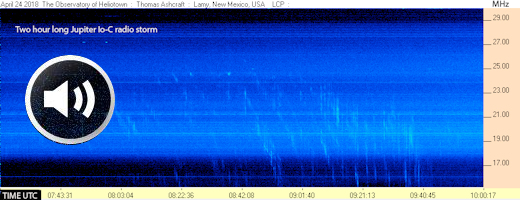
"It was one of the better storms of the year so far," says Ashcraft. "In the audio specimen you can hear the emissions on two of my shortwave radios. One radio is tuned to 21.1 MHz and the other at 18.9 MHz." (Plug stereo headphones into your computer; they will separate the two frequencies into left and right ears.)
Radio storms on Jupiter come from natural radio lasers in the giant planet's magnetosphere. Electrical currents flowing between Jupiter's upper atmosphere and the volcanic moon Io can boost these emissions to power levels easily detected by ham radio antennas on Earth.
Jupiter's outbursts could become more intense in the weeks ahead. Why? Because the distance between Jupiter and Earth is shrinking to a minimum on May 10th. "As Jupiter passes closer to Earth in our orbits, the periodic Io-induced radio storms should get stronger," notes Ashcraft.
To learn more about radio storms on Jupiter, and how you can observe them yourself, visit NASA's RadioJove web site.
FAR-OUT MOTHER'S DAY GIFT: Nothing says "I Love You" like a heart-shaped pendant from the edge of space. On Dec. 31, 2017, the students of Earth to Sky Calculus flew an array of cosmic ray sensors to the stratosphere onboard a giant helium balloon. This pendant went along for the ride:

You can have it for $119.95. The students are selling these pendants as a fund-raiser for their cosmic ray monitoring program--and they make great Mother's Day gifts. All proceeds support atmospheric radiation measurements and hands-on STEM education.
Each pendant comes with a greeting card showing the jewelry in flight and telling the story of its journey to the stratosphere and back again. Mom-satisfaction guaranteed.
Far Out Gifts: Earth to Sky Store
All proceeds support hands-on STEM education
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of
NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com.
On Apr. 25, 2018, the network reported 12 fireballs.
(12 sporadics)
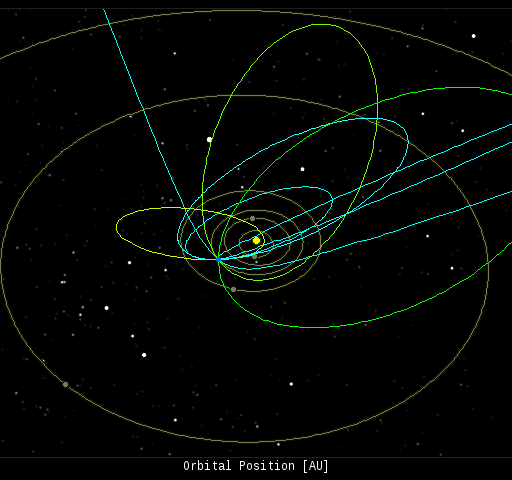
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On April 25, 2018 there were 1907 potentially hazardous asteroids.
 |
Recent & Upcoming Earth-asteroid encounters: | Asteroid | Date(UT) | Miss Distance | Velocity (km/s) | Diameter (m) |
| 2018 HS | 2018-Apr-20 | 5.1 LD | 18.9 | 35 |
| 2018 GS3 | 2018-Apr-20 | 8.5 LD | 19.8 | 24 |
| 2016 JP | 2018-Apr-20 | 12 LD | 12.7 | 214 |
| 2018 HT | 2018-Apr-21 | 7.1 LD | 7.6 | 15 |
| 2018 HL1 | 2018-Apr-21 | 4.7 LD | 14.4 | 55 |
| 2018 GR1 | 2018-Apr-21 | 18.3 LD | 16.4 | 52 |
| 2018 HN | 2018-Apr-21 | 8 LD | 9.8 | 37 |
| 2018 HW1 | 2018-Apr-21 | 0.9 LD | 5 | 23 |
| 2018 HX1 | 2018-Apr-22 | 2.7 LD | 25 | 44 |
| 2018 HV | 2018-Apr-22 | 0.4 LD | 16 | 6 |
| 2018 GG4 | 2018-Apr-23 | 9.8 LD | 14.9 | 20 |
| 2018 HY1 | 2018-Apr-23 | 9.5 LD | 7.6 | 30 |
| 2012 XL16 | 2018-Apr-23 | 15.8 LD | 6.1 | 28 |
| 2018 GH | 2018-Apr-25 | 14.6 LD | 10.7 | 89 |
| 2018 HP | 2018-Apr-26 | 11.6 LD | 10.3 | 19 |
| 2018 GH5 | 2018-Apr-27 | 12.2 LD | 12.7 | 32 |
| 2018 GB2 | 2018-Apr-27 | 17.1 LD | 14.6 | 92 |
| 2013 US3 | 2018-Apr-29 | 10.1 LD | 7.7 | 214 |
| 2018 GO4 | 2018-Apr-29 | 11.8 LD | 8.6 | 40 |
| 2018 GY1 | 2018-Apr-29 | 13.2 LD | 16.7 | 141 |
| 2018 FV4 | 2018-Apr-29 | 17.7 LD | 6.5 | 59 |
| 2002 JR100 | 2018-Apr-29 | 10.8 LD | 7.7 | 49 |
| 2018 HB1 | 2018-May-02 | 10.1 LD | 9.2 | 40 |
| 2018 HR1 | 2018-May-04 | 17.2 LD | 16.3 | 48 |
| 1999 FN19 | 2018-May-07 | 9.7 LD | 5.7 | 118 |
| 2016 JQ5 | 2018-May-08 | 6.3 LD | 10.4 | 9 |
| 388945 | 2018-May-09 | 6.5 LD | 9 | 295 |
| 2018 GR2 | 2018-May-11 | 13.4 LD | 9.8 | 109 |
| 1999 LK1 | 2018-May-15 | 13.3 LD | 10 | 141 |
| 2018 GL1 | 2018-May-18 | 14.3 LD | 5.2 | 67 |
| 68347 | 2018-May-29 | 9.5 LD | 13.3 | 389 |
| 2013 LE7 | 2018-May-31 | 17.8 LD | 1.7 | 12 |
| 2018 EJ4 | 2018-Jun-10 | 5.6 LD | 6.2 | 195 |
| 2015 DP155 | 2018-Jun-11 | 9 LD | 4.4 | 170 |
| 2017 YE5 | 2018-Jun-21 | 15.6 LD | 15.5 | 513 |
| 467309 | 2018-Jun-23 | 17.9 LD | 14 | 355 |
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | Cosmic Rays in the Atmosphere |
Readers, thank you for your patience while we continue to develop this new section of Spaceweather.com. We've been working to streamline our data reduction, allowing us to post results from balloon flights much more rapidly, and we have developed a new data product, shown here:
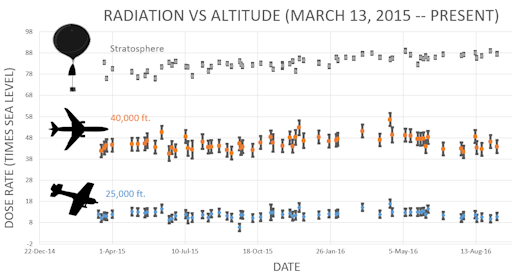
This plot displays radiation measurements not only in the stratosphere, but also at aviation altitudes. Dose rates are expessed as multiples of sea level. For instance, we see that boarding a plane that flies at 25,000 feet exposes passengers to dose rates ~10x higher than sea level. At 40,000 feet, the multiplier is closer to 50x. These measurements are made by our usual cosmic ray payload as it passes through aviation altitudes en route to the stratosphere over California.
What is this all about? Approximately once a week, Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus fly space weather balloons to the stratosphere over California. These balloons are equipped with radiation sensors that detect cosmic rays, a surprisingly "down to Earth" form of space weather. Cosmic rays can seed clouds, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. Furthermore, there are studies ( #1, #2, #3, #4) linking cosmic rays with cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in the general population. Our latest measurements show that cosmic rays are intensifying, with an increase of more than 13% since 2015:
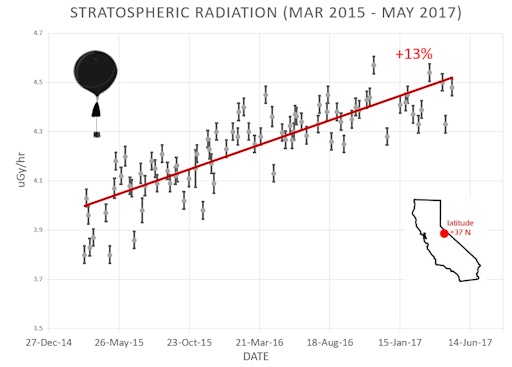
Why are cosmic rays intensifying? The main reason is the sun. Solar storm clouds such as coronal mass ejections (CMEs) sweep aside cosmic rays when they pass by Earth. During Solar Maximum, CMEs are abundant and cosmic rays are held at bay. Now, however, the solar cycle is swinging toward Solar Minimum, allowing cosmic rays to return. Another reason could be the weakening of Earth's magnetic field, which helps protect us from deep-space radiation.
The radiation sensors onboard our helium balloons detect X-rays and gamma-rays in the energy range 10 keV to 20 MeV. These energies span the range of medical X-ray machines and airport security scanners.
The data points in the graph above correspond to the peak of the Reneger-Pfotzer maximum, which lies about 67,000 feet above central California. When cosmic rays crash into Earth's atmosphere, they produce a spray of secondary particles that is most intense at the entrance to the stratosphere. Physicists Eric Reneger and Georg Pfotzer discovered the maximum using balloons in the 1930s and it is what we are measuring today.
| | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | fun to read, but should be taken with a grain of salt! Forecasts looking ahead more than a few days are often wrong. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |
 | Reviews here can help you to pick up best memory foam mattresses. |
| | These links help Spaceweather.com stay online. Thank you to our supporters! |
| | | | | | |

