On October 23rd there will be a partial eclipse of the Sun. Got clouds? No problem. The event will be broadcast live on the web by the Coca-Cola Science Center. | | |
MOSTLY QUIET: New sunspot AR2187 is crackling with minor C-class solar flares. Otherwise, the solar disk is quiet. According to NOAA forecasters, the chance of a major flare today is no more than 1%. Solar flare alerts: text, voice
ORIONID METEOR SHOWER: Last night, Oct. 11-12, NASA's All-Sky Meteor Network detected a piece of Halley's Comet disintegrating in the atmosphere over New Mexico. The fireball was bright enough to see through the light of a bright gibbous Moon:

Multiple cameras tracked the meteoroid, which allowed a calculation of its trajectory: It hit Earth's atmosphere traveling 68 km/s (152,000 mph) and fully disintegrated 67.9 km above Earth's surface.
This fireball is a sign that the Orionid meteor shower is about to begin. Every year in mid- to late-October, Earth passes through a stream of debris from Halley's Comet, the parent of the Orionids. For many nights in a row, pre-dawn sky watchers can see meteors streaking out of the constellation Orion, near the Hunter's shoulder. In 2014, forecasters expect the Orionids to peak on Oct. 21-22 with 20 to 25 meteors per hour.
Stay tuned for updates about meteor activity as Earth approaches the heart of the debris stream.
Meteor alerts: text,
voice Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
FALL COLORS: In most places, the colors of autumn are golden yellow and red, the palette of trees preparing for winter. In Norway, the colors of autumn are different: green and white--that is, auroras over ice. Bernt Olsen photographed them both on Oct. 11th:
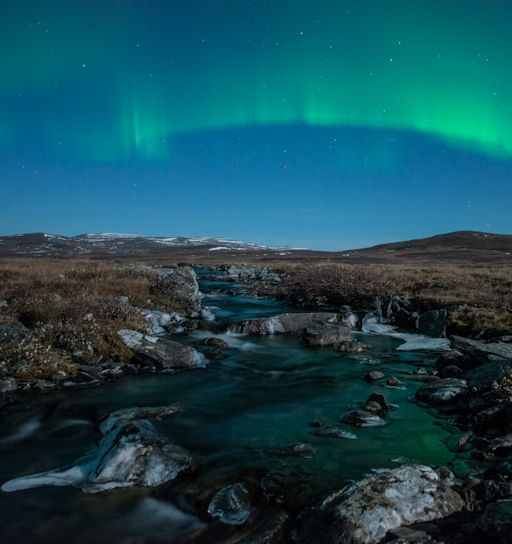

"High up in the Norwegian mountains, at Goulasjavri, close to the Finnish border, the auroras were visible through bright moonlight," says Olsen. "I was able to take the picture despite a cold freezing wind." Aurora alerts: text, voice
Realtime Aurora Photo Gallery
LUNAR ECLIPSE RECORDED BY SOLAR ARRAY: During a lunar eclipse, the normally-bright full Moon darkens as it passes through the shadow of Earth. Millions of sky watchers witnessed this beautiful dimming on Oct. 8th. David Boatwright of Californiia experienced the eclipse in a different way. His solar array browned out:
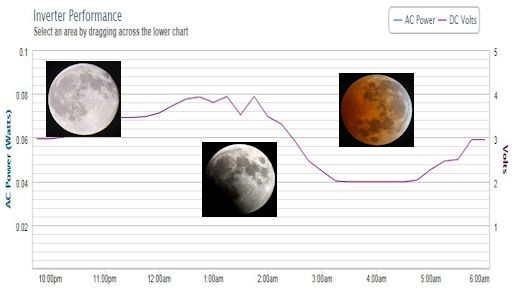
"My home has a 4.5 kW photovoltaic solar system on its roof," he explains. "During the day it produces a good amount of electricity. It even produces a couple of volts from ambient light at night. A full Moon will increase it to nearly 4 volts DC when overhead."
"Pictured above is a screen shot of the power output from my system. As you can see, it recorded the lunar eclipse. The voltage was cut in half during totality. From 3:30am to 4:30am PDT, the DC voltage dropped from 4 volts to 2 volts and then back up to 3 volts at the conclusion of the eclipse. I believe the 1 volt difference, before vs. after the eclipse, is due to the Moon being lower in the sky when the eclipse ended."
"By the way, I was watching the eclipse in my backyard as this voltage drop was occurring," he says.
Realtime Eclipse Photo Gallery
Realtime Space Weather Photo Gallery
Realtime Comet Photo Gallery
Every night, a network of NASA all-sky cameras scans the skies above the United States for meteoritic fireballs. Automated software maintained by NASA's Meteoroid Environment Office calculates their orbits, velocity, penetration depth in Earth's atmosphere and many other characteristics. Daily results are presented here on Spaceweather.com.
On Oct. 12, 2014, the network reported 29 fireballs.
(27 sporadics, 1 Orionid, 1 Southern Taurid)
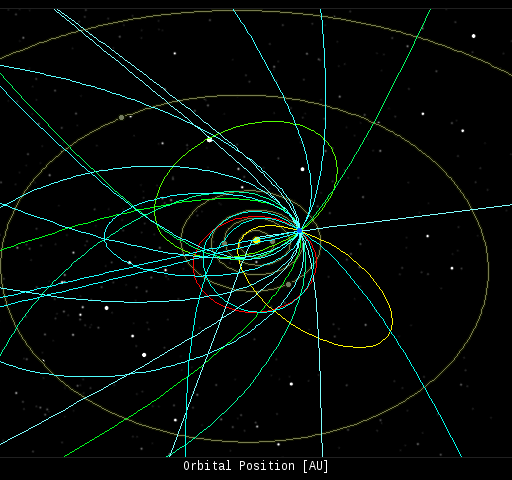
In this diagram of the inner solar system, all of the fireball orbits intersect at a single point--Earth. The orbits are color-coded by velocity, from slow (red) to fast (blue). [Larger image] [movies]
Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (
PHAs) are space rocks larger than approximately 100m that can come closer to Earth than 0.05 AU. None of the known PHAs is on a collision course with our planet, although astronomers are finding
new ones all the time.
On October 12, 2014 there were 1506 potentially hazardous asteroids.
Notes: LD means "Lunar Distance." 1 LD = 384,401 km, the distance between Earth and the Moon. 1 LD also equals 0.00256 AU. MAG is the visual magnitude of the asteroid on the date of closest approach. | | The official U.S. government space weather bureau |
| | The first place to look for information about sundogs, pillars, rainbows and related phenomena. |
| | Researchers call it a "Hubble for the sun." SDO is the most advanced solar observatory ever. |
| | 3D views of the sun from NASA's Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory |
| | Realtime and archival images of the Sun from SOHO. |
| | from the NOAA Space Environment Center |
| | the underlying science of space weather |

